How did we get here? Where are we going? Fundamental questions that should be asked as they tell us who we are. I am of course talking about walls. Wood frame walls are pretty impressive technological creations. How come they look the way that they do? How will they look in the future?
Early on I was a creationist,1 now I am an evolutionist. I am of the opinion that necessity is the mother of all invention and that has principally driven the evolution of wood frame design. But greed and speed are often right there as well. We’ve been building with wood for thousands of years. But in the last two hundred years we have been on a real tear. And if the last twenty years are any indication of what the next twenty are going to be like hold on to your hats.
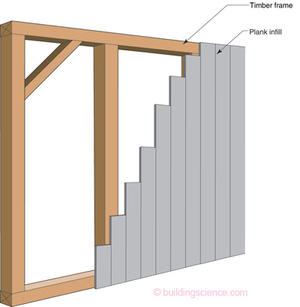
On the evolutionary trail instead of Australopithecines, we will start with timber framing. The technology of timber framing dates back to pre-Roman times and everyone claims it as their own – Japan, England, Scotland, Denmark, Norway, France, Germany.2 Timber framing involved big pieces of wood held together with pegs and interlocking joints (mortise and tenon). Note the word “frame.” A frame has four sides. The timbers bound the four sides of the frame. The wall frames were often infilled with vertical planks along with a whole bunch of other stuff. Diagonal bracing kept the frames from falling over.
Today’s sheathing and cladding (a.k.a. “weatherboarding”) appear to be descended from the original timber frame vertical plank infill. However, they represent two distinct evolutionary branches but with a common ancestor. To understand this we need to look both at the plank infill and the “other stuff” used as infill.

Photograph 1: Stave Church—Borgund, Laerdal, Norway, 12th Century. Image taken by Frode Inge Helland.
Weatherboarding is a term Europeans use to refer to the cladding installed on the exterior of a house consisting of long thin timber boards that overlap one another either vertically or horizontally. The Norwegians and Swedes are well known for their vertical board-and-batten siding the origins of which can be directly traced back to their ancient stave churches (Photograph 1). In the Scandinavian countries the vertical boards were used to protect timber and log structures from weathering. This vertical wood siding weather protection technology made an early appearance in Canada with log “piece sur piece” buildings constructed by the Hudson’s Bay Company.3 In England the practice was to install the weatherboards horizontally in the form of “clapboards.” Clapboards were traditionally “riven boards” – in that they were “split” to their “appropriate thickness.” This technology subsequently made its way to New England with the colonists.4
Big posts or staves take a lot of work and use up timber so folks started to set them farther and farther apart. With the posts or staves getting farther and farther apart horizontal clapboards or weatherboards needed intermediate support between these principal vertical load bearing members and this lead to the introduction of smaller vertical posts spaced more closely together between the larger bigger posts (Photograph 2). It also lead to the introduction of layers of horizontally installed boards – thicker than the clapboards - called sheathing – all for the purpose of supporting the clapboards. So we had two approaches going here. Which one was selected often depended on the presence of a sawmill and the water to power it – the thicker boards tended to be sawn – whereas the clapboards were split and didn’t need a sawmill. Without a sawmill we tended to see more vertical smaller posts spaced more closely together in place of sheathing. We still see this distinction today regionally in the United States and in Australia and New Zealand, no sheathing, just an exterior cladding. Stucco in California is typically installed on open studs supported only by building paper, piano wire and metal lath.

Photograph 2: Exposed Timber Frame—One hundred and fifty year timber frame house being renovated. Exterior horizontal sheathing boards and weatherboards removed. Note the close spacing of the vertical intermediate posts.
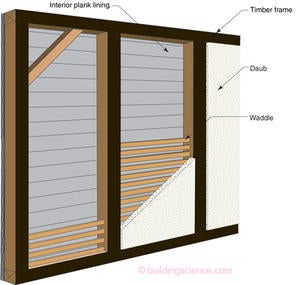
While all of this weatherboard, clapboard and sheathing evolution was going on things were also happening with the “other stuff” used as infill between the posts and staves. This other filling was often referred to as “nogging” and typically took the form of “wattle-and-daub.” Split branches or slats were woven together between vertical stakes creating a lattice (“wattle”) that was traditionally covered with a plaster-like material made of some combination of dirt, clay, sand, animal hair and animal dung and straw (“daub”) (Photograph 3). This technology pre-dates the Greeks and Egyptians. Daubers were the folks who plastered the outside of wood framed buildings.5 The ingredients yield the classic combination of binders, aggregates and reinforcement – combinations that today form the basis of modern stucco.6 Wattle-and-daub panels that infilled exposed timber frames gave us the “classic Tudor” look - lime plaster (white) coatings between tar coated (black) timbers (Photograph 4).

Photograph 3: Wattle-and-Daub—This is a timber frame house in Wales, United Kingdom, with the wattle-and-daub exposed. Note the weaving of the wattle.

Photograph 4: Waltrop House—Germany, 1400, wattle-and-daub infill panels with an exposed timber frame. Wattle-and-daub has a lime plaster coating. Timbers are coated with tar.
The problem with wattle-and-daub was its water sensitivity. It tended to crack and needed to be coated with “white-wash” and lime plaster to keep the water out. Over time the wattle evolved into horizontal wooden lath supported on smaller vertical members called studs. Leaving the timber frame exposed was eventually found to be a bad idea – when the timber frame moved it further cracked the infill wattle-and-daub panels – as it lead to more water entry. As wood frame building technology evolved the timber frames tended to get completely covered with lath-and-daub thereby protecting the timber frame. This compete plastering of the exterior to improve weather resistance became known as pargetting.7 Today we call it stucco, and it is made from Portland cement, sand and water. Sometimes lime is added to increase workability, flexibility and increase water vapor permeability. As an additive lime turns out to be very desirable – a lesson that seems to have been lost in more recent times. Over time the wattle disappeared but the stucco stayed. The wattle as a support for stucco was replaced with horizontal wooden lath and then board sheathing with building paper and a metal lath. It can be argued by that one evolutionary path for sheathing was wattle to wood lath to board sheathing to plywood to OSB to insulating foam-board sheets.
All this sets the stage for three really, really big things that didn’t seem like really, really big things at the time. The place was the American Midwest and the time was the first part of the 19th century. The first really big thing was the shortage of skilled labor. The heartland around 1800 did not have many skilled carpenters or stonemasons or skilled anything. The second really big thing was the development of machine made nails. Nails used to be made by hand by smiths. It was a family cottage industry kind of thing. Really. Then a bunch of American entrepreneurial inventor types came up with machines that could make nails very fast and very cheap. The price of nails fell so fast that by the 1850’s nails cost less in Chicago than the tax on European nails. The third really big thing was the milling of logs into dimensional pieces of lumber – each one the same as the next – and the really important part – these dimensional pieces of lumber were mass-produced.
These three really, really big things lead to one of the greatest construction booms in history and the advent of affordable housing. The nails allowed us to get rid of complex joinery – no more mortise and tenon – and allow relatively unskilled folks to nail together mass produced small sticks (2x4’s and 2x6’s and 2x8’s) spaced closely together in a light frame. All this gets us balloon framing. Balloon framing using dimensional lumber and manufactured nails was so revolutionary that a balloon framed “Illinois cottage” was displayed at the Paris Exhibition of 1867 as a display of American technological prowess.8 Site built stick framing proved to be so fast and so efficient that it dominates residential wood-frame construction worldwide to this day. The only significant changes since have been better tools (skill saws, nail guns) and platform framing which we got in the 1950’s. Oh, some of the exterior and interior linings have changed and we did begin to fill the cavities inherent in frame construction, but the fundamental structural system of walls has not changed much over the past 150 years. It’s those linings and cavity fills that we are going to look at more closely.
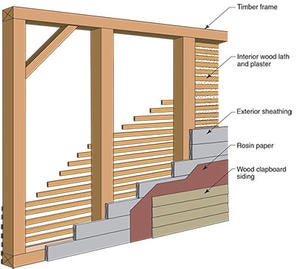
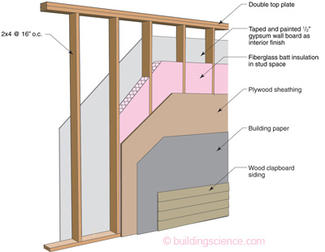
By the beginnings of the 20th century the wood frame wall pretty much looks familiar to many of us. A 2x4 wood fame with studs at 16 inch centers with 1 inch thick board sheathing installed horizontally (sometimes diagonally if any adults were involved or if there was access to a structural engineer) on the exterior and wood lath and plaster on the interior. The cavity is empty. Outside of the board sheathing we typically have clapboards. There may or may not be a building paper between the clapboards and the sheathing. On smaller less expensive “worker cottages” there is often no board sheathing and no building paper just the clapboards. So what was the function of the building paper? Ah, easy question, with clapboards and board sheathing it was to reduce drafts. It was not a water control layer. Amazing, but true. Read the old books. The water control function of building paper seemed to have been introduced in the 1930’s and even then it was not widespread. Think about it, we did not change the I-Codes to require building paper for all houses until after 2000 – less than a decade ago. How did we keep the water out of all those buildings before the use of building paper? We didn’t. They got wet and they dried. Boring, but true. And the first building papers were not good for water control in any event – they were sized rosin paper. Impregnated felts and coated papers came much later.
In the 1950’s the board sheathing began to be replaced with plywood. Then plywood began to be replaced with oriented stand board (OSB) in the 1970’s. The interior wood lath and plaster began to be replaced with plaster covered plasterboard lath in the 1930’s and then with gypsum wallboard in the 1950’s.
Cavity insulation got a pretty inauspicious start in America as compressed eel grass (“Cabot’s Quilt”) at the turn of the last century. Cleaned cattle hair and mineral wool came later followed by cellulose (the best use for the NY Times I can think of). Fiberglass batts came in the 1930’s, first as partial fills and then as full fills. Not much changed until spray foams became popular in the 1990’s. With the exception of spray foams, all the cavity insulations were “convection suppressors” with some radiation control properties – they were not “air barriers.” Air tightness came from either sealing the interior lining (gypsum board) or sealing the exterior sheathing or sealing the polymer-based exterior building “paper” (more recently typically referred to as “house wrap”).
The industry standard wall for most of North America circa 2000 was a 2x4 frame at 16 inch centers with OSB sheet sheathing, a house wrap made from plastic, vinyl or cement board siding (cladding or weatherboard), lined on the inside with gypsum wallboard and insulated within the cavity with a fiberglass batt. The function of the house wrap in this wall assembly is both rainwater control and a contribution to the assembly air tightness. The function of the OSB sheathing is support for the siding, shear resistance for the 2x4 frame and a contribution to the assembly air tightness. The function for the gypsum wallboard is fire resistance, shear resistance for the 2x4 frame and a contribution to the assembly air tightness. The exterior cladding provides aesthetics, ultra-violet radiation protection and mechanical protection.
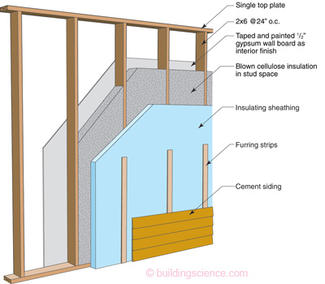
So, now what? The frame wall is undergoing another revolution (okay, it just seems that way because not much has changed in 150 years) – a 2x6 frame at 24-inch centers and single top and bottom plates is likely to replace the conventional 2x4 frame. Why? It is faster and cheaper to build – and it provides a 5.5-inch cavity for insulation rather than a 3.5 inch cavity. Faster and cheaper? How? Ten percent less lumber (board-footage) and 30 percent fewer pieces.
The sheathing and house wrap functions are being combined – we already see hybrid OSB systems with an exterior surface that is also a water control layer. Even more sophisticated are insulating sheathings that combine not only the functions of a sheathing and housewrap but also provide thermal resistance (really, they are sophisticated even though these products were first introduced in the 1950’s). There is even an insulating sheathing available that provides shear resistance.
In terms of cavity insulation we are seeing a trend away from fiberglass batts to spray applied systems. Some spray foams are being promoted as not only providing cavity insulation and air tightness but also structural properties related to shear and impact resistance. Wow.
I see the industry standard wall for most of North America circa 2015 being 2x6 “advanced frame” at 24-inch centers with exterior foam insulating sheathing and a spray applied cavity insulation lined with gypsum board (Photograph 5). And for us more “progressive” folks – I see a much greater thickness of exterior insulating sheathing and a hybrid cavity fill – an R-50 wall. That’s what a thousand years of evolution will get you.

Photograph 5: Building America—Advanced frame 2x6 structure, studs on 24 inch centers, single top and bottom plates, 1.5 inches foil faced polyisocyanurate insulating sheathing. Cavity insulation not yet installed. This is likely to be the industry standard in the next decade. R&D courtesy of the US DOE Building America Program.
One Thousand Years of Evolution |
Palisade Wall
|
Timber Frame |
Wattle and Daub |
Clapboard Timber Frame |
Platform Frame |
Advanced Frame |
Footnotes:
In the beginning there was cold and wet, and Hutcheon and Handegord said let there be an enclosure that separates the inside from the outside, and Timusk saw that it was good…
If you believe archaeologists (I mean when have they ever not been right?) timber framing seems to have evolved from “palisade” construction where logs were embedded in the ground vertically side-by-side supporting a roof. Over time the logs got farther and farther apart and became known as posts. In Old Norse load bearing posts were called “stafr” which gave rise to the term “stave” construction. To keep the posts from rotting it was found that you could support them on stones and from there it was found the posts could be supported on a raised sill frame resting on lots of stones and from there we got rubble foundations. There is a really nice discussion of this on Wikipedia (http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Stave_church).
Horizontal timber (or log) construction was introduced to North America by the French; as such it is not a distinct “New World” technology. Log construction in the New World broke into two distinct types: the American “interlocking corner” approach and the Canadian (and obviously more superior) “horizontal construction with corner posts.” Both were readily displaced by timber framing due the savings in materials – much less timber is used with timber frame construction than with horizontal log construction.
It has been argued that it happened the other way around. The term clapboards comes from the Dutch “klaphout” (klappen, to split, crack). It originally referred to clapboard oak staves used to make barrels. Historically the English got their oak from the Baltic, but this changed with the settlement of the colonies - New England had a lot more oak than almost anywhere else. Legend has it that the first cargo shipped from Jamestown back to England included clapboards for barrel making. The argument goes that colonists, not happy with wattle-and-daub infill over their timber frame buildings, installed clapboards on the outside walls for better weather protection. I’ll buy all of this except for the part that the clapboards weatherboarding idea originated in New England. It seems to have been in use much earlier in the eastern parts of England (Norfolk, Suffolk, Essex, familiar names to the Yanks who were stationed there during the Second World War with the Eighth Air Force). If you have lots of wood available to you, why use wattle-and-daub infill? Even the ancestry of the Dutch name ties in with Dutch and Danish settlements in East Anglia (the aforementioned Norfolk, Suffolk…).
Frank Nunes, when I refer to you as a “dauber” I am not insulting you…it was an honorable old profession and you are certainly getting older…
Guess what the animal dung was for? Never mind, this will get edited out anyway.
Pargeting is often referred to as the decorative relief in the plaster itself. Many plasters were applied with elaborate decorative patterns. Use of the term varies with geography and age. I was taught that a “parge” coat was the cementious rendering applied to the exterior of masonry foundation walls (to reduce groundwater entry) or to the interior of masonry mass walls (to reduce air leakage and water penetration), and finally to the interior of chimneys to improve gas tightness.
Professor Ted Cavanagh of Dalhousie University argues that balloon framing was not invented by George Washington Snow or Augustine Taylor as Chicagoans tell it – but that its origins are distinctly French. He argues that balloon framing has its origins in “maison en boulin” construction – a type of French Missouri construction used in towns along the Mississippi River. In that case it would have been a delicious irony that balloon framing’s “coming out party” was in Paris as an example of American innovation. But regardless of its’ origins Chicago sure got balloon framing on the map – it jump started the technology. Mrs. O’Leary’s cow helped. When Chicago burned down in 1871 it needed to be rebuilt. Guess which technology was used? Check out this link (http://www.americanheritage.com/articles/magazine/it/1999/4/1999_4_50.shtml).